About vitamin E (tocopherol and tocotrienol)
Contents
◆ Definition of vitamins
◆ Functions of each vitamin
◆ Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant
◆ Free radicals cause aging and disease
◆ Vitamin E efficiently scavenges free radicals
◆ Vitamin E is a generic name for eight compounds
◆ Vitamin E was discovered as an antisterility factor
◆ How to distinguish between natural and synthetic products
◆ In vivo activity differences between natural and synthetic products
◆ Super vitamin E: Tocotrienol
◆ Definition of vitamins
Vitamin is a general term for organic compounds other than carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
that are essential nutrients for living organisms.
Most vitamins cannot be synthesized in the human body, and thus must be obtained from food.
Vitamins are classified into two groups; one is fat-soluble and the other is water-soluble.
[Fat-soluble vitamin]
Vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and vitamin K
[Water-soluble vitamin]
Vitamin B1, vitamin B2, niacin, pantothenic acid, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, folic acid, biotin, and vitamin C
◆ Functions of each vitamin
The function of each vitamin is as follows.
| Fat-soluble/ water-soluble |
Vitamin | Function |
| Fat-soluble | Vitamin A | Maintains night vision, healthy skin, and mucous membranes. |
| Vitamin D | Promotes calcium absorption in the intestinal tract and aids in bone formation. | |
| Vitamin E | Acts as an antioxidant to protect lipids in the body from oxidation and help to maintain cellular health. | |
| Vitamin K | Maintains blood coagulation ability. | |
| Water-soluble | Vitamin B1 | Helps to produce energy from carbohydrates and maintain healthy skin and mucous membranes.炭 |
| Vitamin B2 | Helps to maintain healthy skin and mucous membranes. | |
| Niacin | Helps to maintain healthy skin and mucous membranes. | |
| Pantothenic acid | Helps to maintain healthy skin and mucous membranes. | |
| Vitamin B6 | Helps to produce energy from protein and maintain healthy skin and mucous membranes. | |
| Vitamin B12 | Aids in the formation of red blood cells. | |
| Folic acid | Aids in the formation of red blood cells. Contributes to the normal development of the fetus. | |
| Biotin | Helps to maintain healthy skin and mucous membranes. | |
| Vitamin C | Helps to maintain healthy skin and mucous membranes. Acs as an antioxidant. |
◆ Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant
Phytochem Products Inc. extracts functional ingredients such as vitamin E from inedible biomass
which is a by-product in manufacturing process of rice bran oil.
The most important and characteristic role of vitamin E is antioxidation.
Thus, vitamin E is widely used in foods and cosmetics as an antioxidant agent.
Vitamin E is an essential vitamin for maintaining youth.
To begin with, what phenomenon is aging?
How does it occur?
To understand the role and importance of vitamin E, it is necessary to learn about
the damage to living tissue caused by free radicals*.
(*) A free radical is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron.
Due to these unpaired electrons, free radicals are chemically unstable and highly reactive.
◆ Free radicals cause aging and disease
When humans take in oxygen through breathing, free radicals with unpaired electrons such as
superoxide anion (・O2–) and hydroxyl radical (・OH) are necessarily generated in the metabolic process.
These are a kind of “reactive oxygen species (ROS)”.
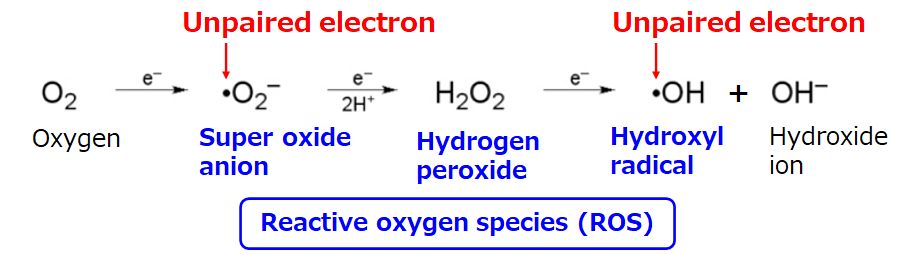
Free radicals are indispensable for our vital activities because they have some important roles
such as protection of our body from bacteria/viruses and transmission of information between cells.
On the other hand, free radicals are highly reactive and they indiscriminately attack our important
biological components such as lipids, proteins, and DNA.
In particular, hydroxyl radicals (・OH)are the most reactive (= the most harmful) free radicals to living organisms.
Damaged cells are usually repaired.
However, if the number of damaged cells is too large, the repair process may not be able to keep up,
or DNA may be mis-replicated.
It leads to aging and cancerization of cells.
Injury, illness, stress, smoking, and heavy alcohol consumption can also generate excessive free radicals in the body.
◆ Vitamin E efficiently scavenges free radicals
Vitamin E scavenges these free radicals as an antioxidant to prevent oxidation of lipids in our body,
which leads to protect the body from the various diseases and DNA mutation/damage.
When lipids (LH) are attacked and oxidized by free radicals, lipid radicals (・L) are generated.
They react with oxygen to generate lipid peroxyl radicals (・LOO) and lipid peroxides (LOOH).
These lipid radicals and lipid peroxyl radicals then oxidize other lipids to generate
new free radicals in a chain reaction.
Lipids oxidized by free radicals can cause various diseases such as atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction.
Vitamin E prevents the onset of such diseases by scavenging excess free radicals and
breaking the chain reaction of lipid oxidation.
Vitamin E acts as a lipid-soluble radical scavenger primarily in cell membranes.
Cell membranes are made of lipids and are constantly under attack by free radicals.
Vitamin E protects cell membranes and the DNA in the nucleus of the by scavenging free radicals
that cause lipid oxidation reactions in the cell membrane to prevent cancer and mutation of cellular tissues.
On the other hand, water-soluble antioxidants such as vitamin C and uric acid capture radicals
that exist in the outer water layer of the cell membrane.
Although they cannot capture fat-soluble radicals inside the cell membrane, vitamin C plays an important role
to regenerate vitamin E that has lost its antioxidant activity.
◆ Vitamin E is a generic name for eight compounds
Vitamin E is the generic name for eight different compounds: four tocopherols (α, β, γ, and δ) and four tocotrienols.
Both tocopherols and tocotrienols have a moiety called the chroman ring and a long carbon side chain.
The side chain of tocopherols has all single bonds, whereas that of tocotrienols has three double bonds.
The α, β, γ, and δ forms are distinguished by the position and number of methyl groups (R1, R2: CH3-) in the chroman ring.
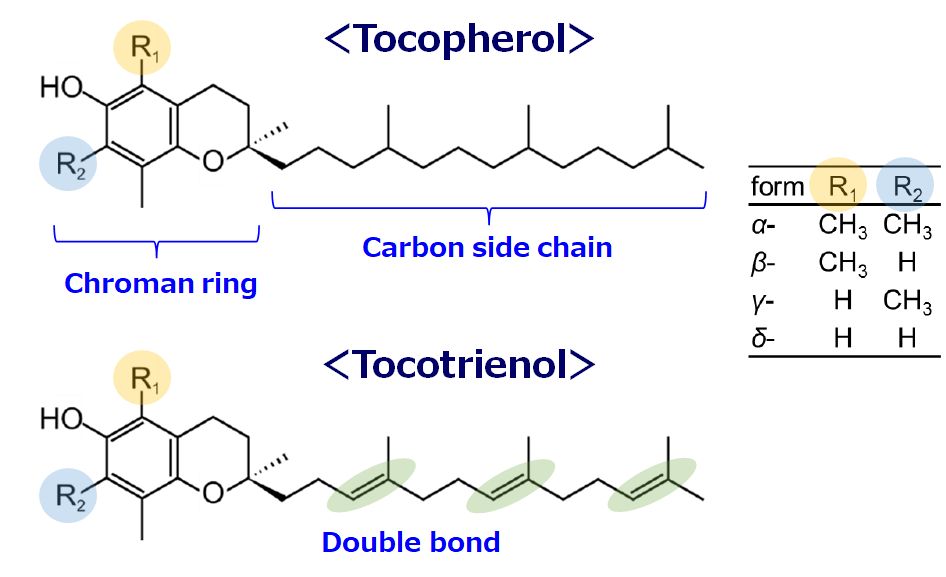
Of the eight vitamin E compounds, alpha-tocopherol is the most well-known.
It is the most abundant vitamin E compound in nature and the most active in vivo.
As described below, α-tocopherol is the first discovered vitamin E as an antisterility factor.
◆ Vitamin E was discovered as an antisterility factor
Vitamin E was originally discovered as a factor in improving infertility in rats.
Rats fed a vitamin E-deficient diet had impaired reproductive function, which was recovered
when the rats were fed fresh lettuces and wheat germs.
In subsequent studies, the component that improves infertility in rats was isolated and identified.
It was named “tocopherol”.
The name “tocopherol” is derived from the Greek words tókos (birth) + phérein (carry),
and was coined by combining “ol”, which indicates the presence of a hydroxy group (-OH).
Later, other isomers of tocopherols were also isolated one after another.
The first isolated compound was called α-tocopherol, and the ones discovered later were called β- and γ-tocopherol.
◆ How to distinguish between natural and synthetic products
Of the eight vitamin E compounds, only α-tocopherol is synthetically produced and marketed.
α-Tocopherol is widely contained in pharmaceuticals, foods, and feeds for the purpose of disease prevention
and treatment, nutritional supplementation, and antioxidation.
More than 90% of them are synthetic.
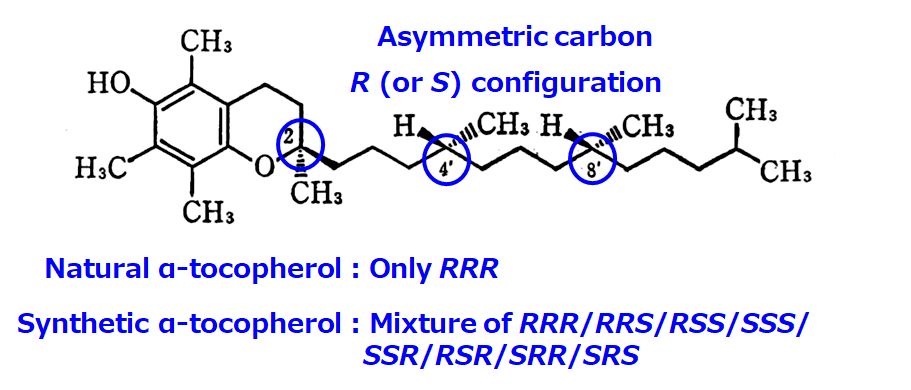
Naturally occurring α-tocopherol exists as a single stereoisomer (RRR-α-tocopherol), whereas synthetic one is
an equimolar mixture of eight stereoisomers (RRR-/RRS-/RSS-/SSS-/SSR-/SRR-/SRS-/RSR-α-tocopherol).
These seven isomers other than RRR-α-tocopherol do not exist in nature.
To distinguish whether α-tocopherol is natural or synthetic, look at the following indications.
Natural: D-alpha-tocopherol
Synthetic: DL-alpha-tocopherol
Natural products have only the initial letter D (or d), but synthetic ones have two letters DL (or dl).
If it says “derived from soybeans” or “derived from vegetable oil”, it is a natural product.
If it says only “α-tocopherol” or “vitamin E” without “D” or “DL”, it is almost certainly a synthetic product.
◆ In vivo activity differences between natural and synthetic products
Natural and synthetic α-tocopherols have different activities when ingested into the body.
Synthetic α-tocopherol, a mixture of eight stereoisomers, has only half the biological activity of natural α-tocopherol.
It is also known that natural α-tocopherol reaches the fetus through the placenta three times more efficiently
than synthetic α-tocopherol.
From these facts, it is thought that our body has a mechanism to recognize D-α-tocopherol (RRR),
which originally exists in nature, and selectively utilize it.
◆ Super vitamin E: Tocotrienol
Vitamin E family is divided into two groups: tocopherols and tocotrienols.
Tocotrienol was first isolated more than 25 years after α-tocopherol was discovered.
Until now, the term “vitamin E” has been used for denoting only α-tocopherol in most cases
because it is the most abundant form of vitamin E in nature, and thus research on vitamin E has focused on α-tocopherol.
On the other hand, tocotrienol is a rare component contained in very small amounts in a limited number of
vegetable oils such as palm oil, rice bran oil, and barley oil.
Because tocotrienols are expensive and there are no synthetic products, research on tocotrienols
has lagged far behind that on tocopherols.
Tocotrienols have three double bonds in the carbon side chain, which gives tocotrienols some characteristic properties.
Tocotrienol is called “super vitamin E” because it shows 40-60 times higher antioxidant activity than tocopherol.
The excellent effects of tocotrienols have gradually begun to attract attention since 1990.
Some unique functions of tocotrienols such as cholesterol-lowering and anticancer effects,
which are not found in tocopherols, have been revealed.
Tocotrienols are excellent antioxidants and have been reported to have the following health and beauty benefits.
| Foods | Improvement of skin condition (moisture, smoothness, elasticity) Prevention of arteriosclerosis Neuroprotective action Increase in hair volume Immunity activating effect Lowering of serum total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol Protection and improvement of liver function Prevention and improvement of stroke Prevention of carcinogenesis and inhibition of cancer cell proliferation |
|---|---|
| Cosmetics | Inhibition of skin redness and pigmentation caused by ultraviolet rays (whitening and sunburn prevention) Protection of epidermal cells from ultraviolet rays and active oxygen (anti-oxidation, anti-aging) Promotion of dermal fibroblast and hyaluronic acid production (anti-aging, maintenance of firmness and elasticity) |
Although these benefits of tocotrienols have been gradually revealed, most studies have been conducted
using mixtures of tocotrienols and tocopherols.
Few experiments using tocotrienols alone have been performed and the functions of each isomer of tocotrienols
have not been fully elucidated yet.
Further studies are expected in the future.
